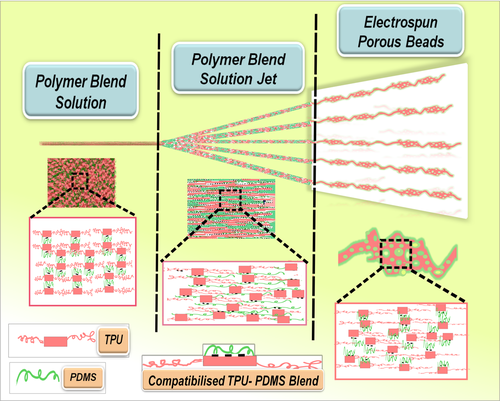
Composition and architecture of scaffolds are the most important factors determining the performance of skin substitutes. In this work, morphology induced unique physical and biological characteristics of compatibilized TPU–PDMS blend scaffolds at 90:10, 80:20, and 70:30 blend ratios of TPU and PDMS was studied. The fiber morphology, porosity, surface wettability, and mechanical properties of electrospun scaffolds were distinctly influenced by the presence of PDMS. Interestingly, the scaffold architecture varied from electrospun fibers to porous fibers and finally occurrence of unique porous beads noticed at 30% PDMS in the microstructure which was confirmed using FESEM. Micro-CT analysis revealed that the porosity of electrospun scaffolds was enhanced from 61% to 79% with 30 parts of PDMS addition. Moreover, MTT assay and cell proliferation were studied using human skin fibroblast cells and found to be significantly enhanced with the PDMS percentage. TPU–PDMS blends offer better overall performance at 70:30 blend ratio of TPU and PDMS (T70P30). Only 4% of hemolysis was observed for T70P30 blends, which establishes the hemocompatibility of the material. In comparison, the results reveal the potential of the cytocompatible T70P30 scaffold for the fabrication of skin substitutes for tissue engineering applications. © 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. J Biomed Mater Res Part B: Appl Biomater 107B: 1634–1644, 2019.


